
The researchers found that additional studies of the data from Curiosity show that non-biological sources they had considered don’t fully explain the organics. They conclude, therefore, that a biological source is a reasonable hypothesis.
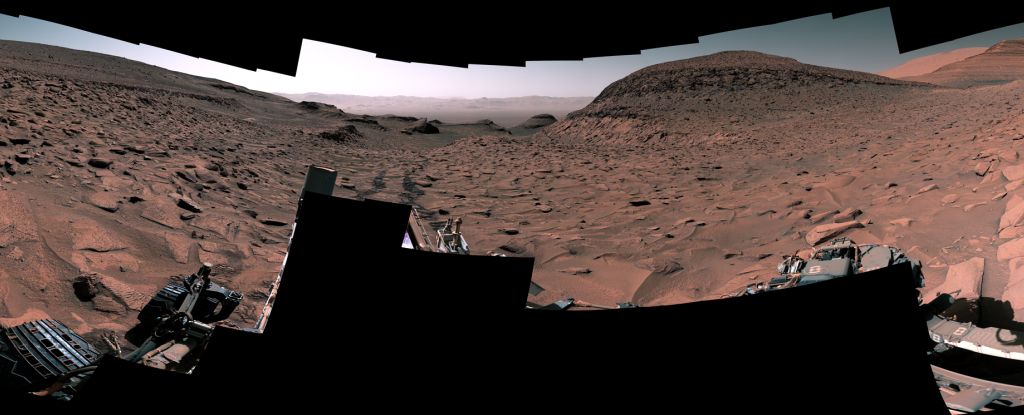

A surprise discovery in Gale Crater is the component that was missing in the puzzle of Mars's climate history.

The discovery is one of the most significant findings in the search for evidence of past life on Mars.

The mineral content of oddly pale rocks found in Jezero Crater can only have formed under very warm, very soggy conditions – suggesting that, long ago, Mars may have been a lot more peculiar than we ever suspected.
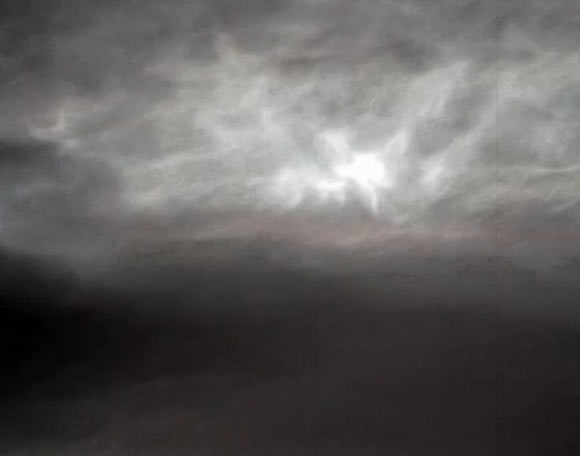

New images, taken over 16 min on January 17, 2025 by the Mastcam instrument on NASA's Curiosity rover, show noctilucent, or twilight clouds, in the atmosphere of Mars.

We know that lakes existed on Mars’ surface billions of years ago. But scientists have debated whether the lakes were open to the air or covered by a layer of ice.

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover viewed these yellow crystals of elemental sulfur using its Mast Camera. The discovery marks the first time this mineral has ever been found in a pure form on Mars.

Among several recent findings, the rover has found rocks made of pure sulfur — a first on the Red Planet.
The mystery of life’s origins on Earth has long puzzled scientists, but a recent discovery on Mars might be shedding new light on this profound question, while also inching closer to finding life on Mars.

New observations of mud cracks made by NASA's Curiosity rover show that high-frequency, wet-dry cycling occurred in early Martian surface environments.

A recent study finds that the vast subsurface fracture networks in Gale crater would have provided water-rich and radiation-shielded conditions that were potentially more habitable than those on the surface.

Raging megafloods, likely triggered by the heat of a meteoritic impact, roared across Gale Crater near the equator of Mars some 4 billion years ago, creating gigantic sedimentary ripples visible today.

NASA's Curiosity rover discovered "startlingly high amounts of methane in the Martian air" on Wednesday in what could potentially be a sign of life on the Red Planet, the New York Times reported on Saturday.

Clay often forms in the presence of water – a key ingredient for the evolution of life as it is known on Earth – and Curiosity’s latest findings add more evidence that a significant amount of water once pooled and flowed in Gale Crater on Mars.

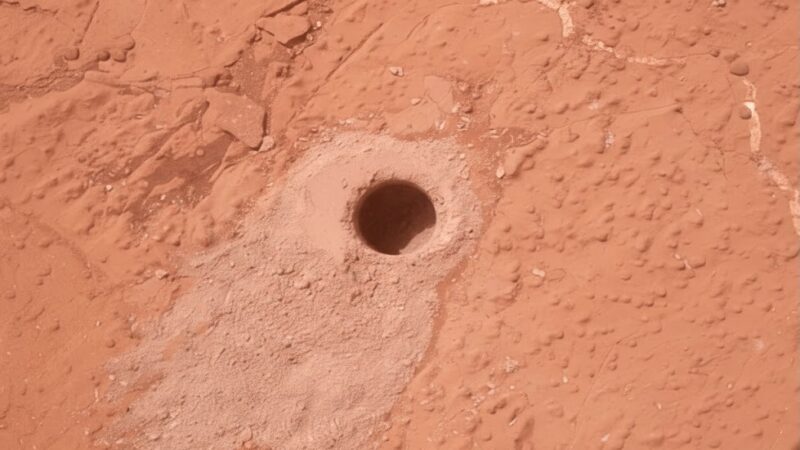
Curiosity Mars rover has started drilling into a clay-bearing unit on the lower slopes of Mount Sharp, while the InSight's mole ran into a sub-surface obstacle of some sort on 28 February after hammering its way just 30 cm into Martian soil.